Evaluating the Carbonation of Concrete by TOC Solid Sample Measurement System
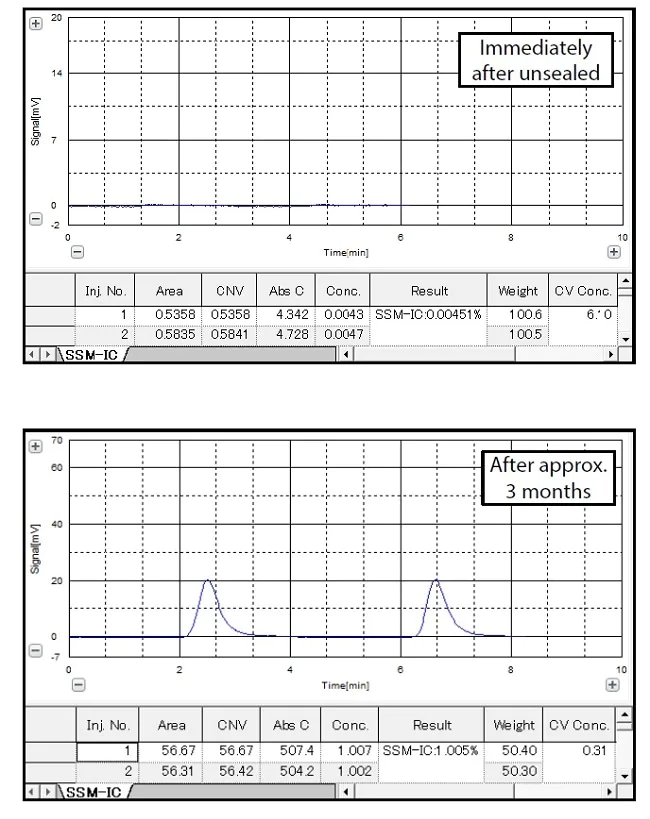
In modern society, concrete is an indispensable material for public works and construction. It is applied to a variety of projects including buildings, roads, and tunnels. Concrete is obtained by mixing and hardening cement, aggregates, and water, so it is very sturdy, but can deteriorate for a variety of reasons including voids and cracks. One of the greatest causes of deterioration is known to be carbonation. Concrete contains a large amount of calcium, so it is normally strongly alkaline. However, when it absorbs carbon dioxide from the air, it turns into calcium carbonate, and gradually becomes neutralized. For this reason, in studying how to improve concrete products and in materials development, it is important to reliably assess the amount of calcium carbonate in materials in order to quantitatively evaluate carbonation. This article introduces an example of the evaluation of the carbonation of a standard sample of cement, which is a component of concrete, by evaluating the amount of inorganic carbon (IC) using the TOC solid sample measurement system.