Sales Rep Locator
AIRsight Infrared Raman Microscope - Support
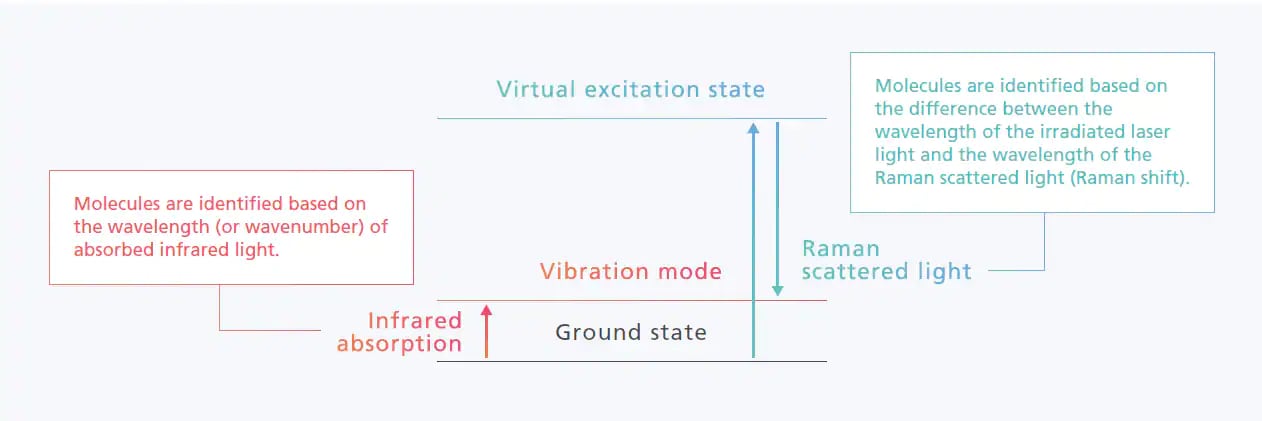
Infrared Spectroscopy and Raman Spectroscopy
Differences between Infrared Spectroscopy and Raman Spectroscopy
Infrared Spectroscopy
Samples are irradiated with infrared light to measure how much light is transmitted through the sample and how much is absorbed.
Raman Spectroscopy
Samples are irradiated with laser light to measure the amount of Raman scattering that occurs from the sample.
| Polar bonds are more sensitive to IR spectroscopy | Non-polar bonds are more sensitive to Raman spectroscopy |
|---|---|
| Polar bonds O-H, N-H, C=O, C-O-C |
Non-polar bonds C=C, S-S, C-S |
Enables Acquisition of Mutually Complementary Molecular Information
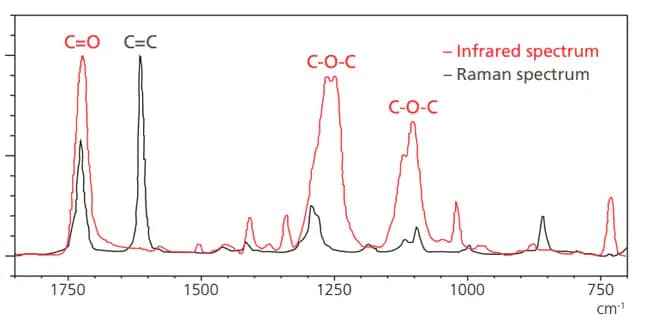
Infrared and Raman Spectra of Polyester
(Laser Wavelength: 532 nm)
Infrared Spectroscopy
Applicable samples
Plastics, organic food components, and some inorganic components
Benefits
- Extensive spectral libraries available to quickly identify a sample
- Nondestructive technique
- ATR (optional), transmission, or reflection methods can be selected depending on the sample
- Polymers and Rubber Materials
Raman Spectroscopy
Applicable samples
Carbon materials (CNT, DLC, diamond, etc.), pigments, additives and other inorganic substances, and some organic substances
Benefits
- Especially well-suited for analyzing carbon materials (carbon nanotubes, diamond, etc.)
- Depth profiling analysis available
- Measure samples directly in some containers because transparent materials (glass, quartz, etc.) do not absorb the laser light or scattered radiation
- High spatial resolution
- Aqueous solutions can be measured


