Analysis of Pesticides & Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) in Drinking Water

Pesticides, also including herbicides and other organic chemicals, along with persistent organic pollutants (POP) have the potential to contaminate drinking water supplies. Pesticides and herbicides may be found in areas such as the Midwestern States with source waters that are impacted by agricultural runoff. POP, sometimes referred to as chemicals of emerging concern (CEC) include industrial organic compounds and pharmaceuticals, that are pervasive and bio-accumulate making them toxic or harmful to aquatic life or humans. PFAS is an example of a POP.
There are several EPA approved methods used to determine these various pollutants. In the EPA approved methods, most are determined using chromatography techniques using selective detectors.
Selected analytes, the approved methods and required instruments are follows
| Chlorinated Phenoxy Herbicides | EPA Method 515, SM 6640 B, or ASTM D5317 | GC-ECD |
|---|---|---|
| Chlorinated Pesticides | EPA Method 508.1 | GC-ECD |
| EPA Method 505 | GC-ECD | |
| EPA Method 525.2 | GC-MS | |
| Nitrogen-phosphorus Pesticides | EPA Method 507 | GC-ECD or GC-NPD |
| EPA Method 525.2 | GC-MS | |
| Carbamate Pesticides | EPA Method 531.2 | HPLC with Pickering Reagent |
| Diquat | EPA Method 549.2 | HPLC with UV Detector |
| Endothall | EPA Method 548.1 | GC-MS |
| EPA Method 525.2 | GC-MS |
Additionally, there are more sophisticated techniques using LC-MS/MS or GC-MS/MS that are not approved but may be used for non-compliance monitoring. We recommend these methods, when allowed, because they can test for different classes of organic chemicals with very little sample preparation, saving time and reducing analytical cost.
| Polar Pesticides, Herbicides, and Carbamates | ASTM D8574 | LCMS-8060RX |
|---|---|---|
| Organochlorine Pesticides and PCBs | ASTM D8543 | GCMS-TQ8050 NX |
Featured Applications
Analysis of Glufosinate, Glyphosate, and AMPA in Tap Water Using Triple Quadrupole LC/MS/MS
Glufosinate is widely used as an amino acid-based herbicide, and glyphosate is a widely-used foliage-applied herbicide. Glyphosate forms the aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) when metabolized in soil or water. As of March 2021, glufosinate, glyphosate, and AMPA are included in “Pesticides” (Item 15) of the target setting items in “Complementary Items to Set the Targets for Water Quality Management” established by Japan’s Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW), with targets values of 0.02 mg/L for glufosinate and 2 mg/L for glyphosate and AMPA. As the analysis method, “Simultaneous analysis by derivatization-solid phase extraction-liquid chromatograph-mass spectrometer” is specified in Appendix Method 22 of Inspection Methods for Complementary Items. This article introduces an example of an analysis of glufosinate, glyphosate, and AMPA without concentration by solid-phase extraction (SPE) specified in Appendix Method 22 using a Shimadzu LCMS-8050. A satisfactory recovery rate was obtained for all three compounds at a concentration of 0.2 μg/L, which is 1/100 of the target value or less, confirming that highly precise analysis is possible.
High Speed Analysis of Pesticides Listed in Appendix Method 20-2 for the Complementary Items for Water Quality Management in Japan Using a Triple Quadrupole LC/MS/MS
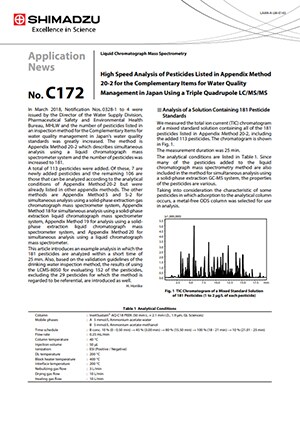
In March 2018, Notification Nos. 0328-1 to 4 were issued by the Director of the Water Supply Division, Pharmaceutical Safety and Environmental Health Bureau, MHLW and the number of pesticides listed in an inspection method for the Complementary Items for water quality management in Japan's water quality standards was greatly increased. The method is Appendix Method 20-2 which describes simultaneous analysis using a liquid chromatograph mass spectrometer system and the number of pesticides was increased to 181. A total of 113 pesticides were added. Of these, 7 are newly added pesticides and the remaining 106 are those that can be analyzed according to the analytical conditions of Appendix Method 20-2 but were already listed in other appendix methods. The other methods are Appendix Method 5 and 5-2 for simultaneous analysis using a solid-phase extraction gas chromatograph mass spectrometer system, Appendix Method 18 for simultaneous analysis using a solid-phase extraction liquid chromatograph mass spectrometer system, Appendix Method 19 for analysis using a solid phase extraction liquid chromatograph mass spectrometer system, and Appendix Method 20 for simultaneous analysis using a liquid chromatograph mass spectrometer. This article introduces an example analysis in which the 181 pesticides are analyzed within a short time of 25 min. Also, based on the validation guidelines of the drinking water inspection method, the results of using the LCMS-8050 for evaluating 152 of the pesticides, excluding the 29 pesticides for which the method is regarded to be referential, are introduced as well.
Analysis of Iminoctadine, Paraquat, and Diquat in Tap Water Using Triple Quadrupole LC/MS/MS [LCMS-8050]
Iminoctadine is used as an antimicrobial agent, and paraquat and diquat are used as non-selective herbicides. By the director of Water Supply Division, Health Service Bureau, Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (0325 No. 3 to 6) in March 2015, a notification of "simultaneous analysis using solid-phase extractionliquid chromatograph-mass spectrometer" (appendix method 21) was issued as a method for testing the presence of these three pesticides in tap water. This article describes an example of analysis of iminoctadine, paraquat, and diquat performed according to appendix method 21. Also described is an investigation into a simplified method that omits part of the sample pretreatment process.